Home> Additional Products > The different types of glazing
TYPES OF GLAZING
High-performance, attractive solutions


Home> Additional Products > The different types of glazing
TYPES OF GLAZING
High-performance, attractive solutions
Many glazing combinations are available, and it can be difficult to navigate! However, the choice of glazing, with the functions it combines, is essential for the performance and benefits expected from the window.
Through 3 key points, let’s discover how to properly define your glazing.
Axis 1. Energy needs:
Double glazing is equipped with metal oxide layers that are sprayed onto the surface of one of the internal faces. Traditionally, these layers are called low emissivity (LE), and the first versions introduced on the market helped reduce heat loss to the outside by half. Today, many variations exist and allow you to adjust the four characteristics below according to your needs:
- Thermal insulation: The type of LE layer helps reduce heat loss to the outside, such as in winter when the house is heated.
- Solar gains: Depending on the chosen LE layer, it is possible to increase solar gains, thus reducing heating needs.
- Solar control: In contrast to solar gains, the goal here is to reduce solar heat gain to limit the need for air conditioning.
- Brightness: LE layers influence the amount of light entering the home.
Below are the different LE layers available and their key characteristics, to be chosen based on your needs: (To learn more about the Eclaz range of glazing, click here.)
| Type of LE layer | Thermal insulation Reduction of thermal losses |
Solar gains Reduction of heating needs |
Solar control Reduction of air conditioning needs |
Light transmission Lighting needs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FE (standard+ Planitherm XN ou équiv.) | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ |
| FE ONE | +++++ | ++ | +++ | + |
| Eclaz Lumi | +++ | +++++ | - | ++++ |
| Eclaz Zen | +++++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| Eclaz Sun | +++++ | + | +++++ | + |
| Cool Lite Xtreme (61/29) | +++ | - | +++++ | - |

Composition type 4/16 Argon/ Eclaz Lumi 4
- Thermal insulation Ug = 1.1 W/(m².K)
- Winter solar factor Scg = 71%
- Light transmission Tlg = 83%

Composition type 4 Eclaz Zen/16 Argon/4
- Thermal insulation Ug = 1.0 W/(m².K)
- Winter solar factor Scg = 53%
- Light transmission Tlg = 80%

Composition type 4 Eclaz Sun/16 Argon/4
- Thermal insulation Ug = 1.0 W/(m².K)
- Summer solar factor Scg = 39%
- Light transmission Tlg = 72%
Axis 2. THE FUNCTION:
Safety glazing:
Standard glass in a monolithic layer breaks into sharp pieces, posing a risk of injury. To prevent these risks, tempered glazing (a protective function for people) can be used. Laminated glazing, consisting of two layers of glass separated by a polymer film, is available and offers a wider range of protection, from safeguarding individuals to protecting against break-ins:
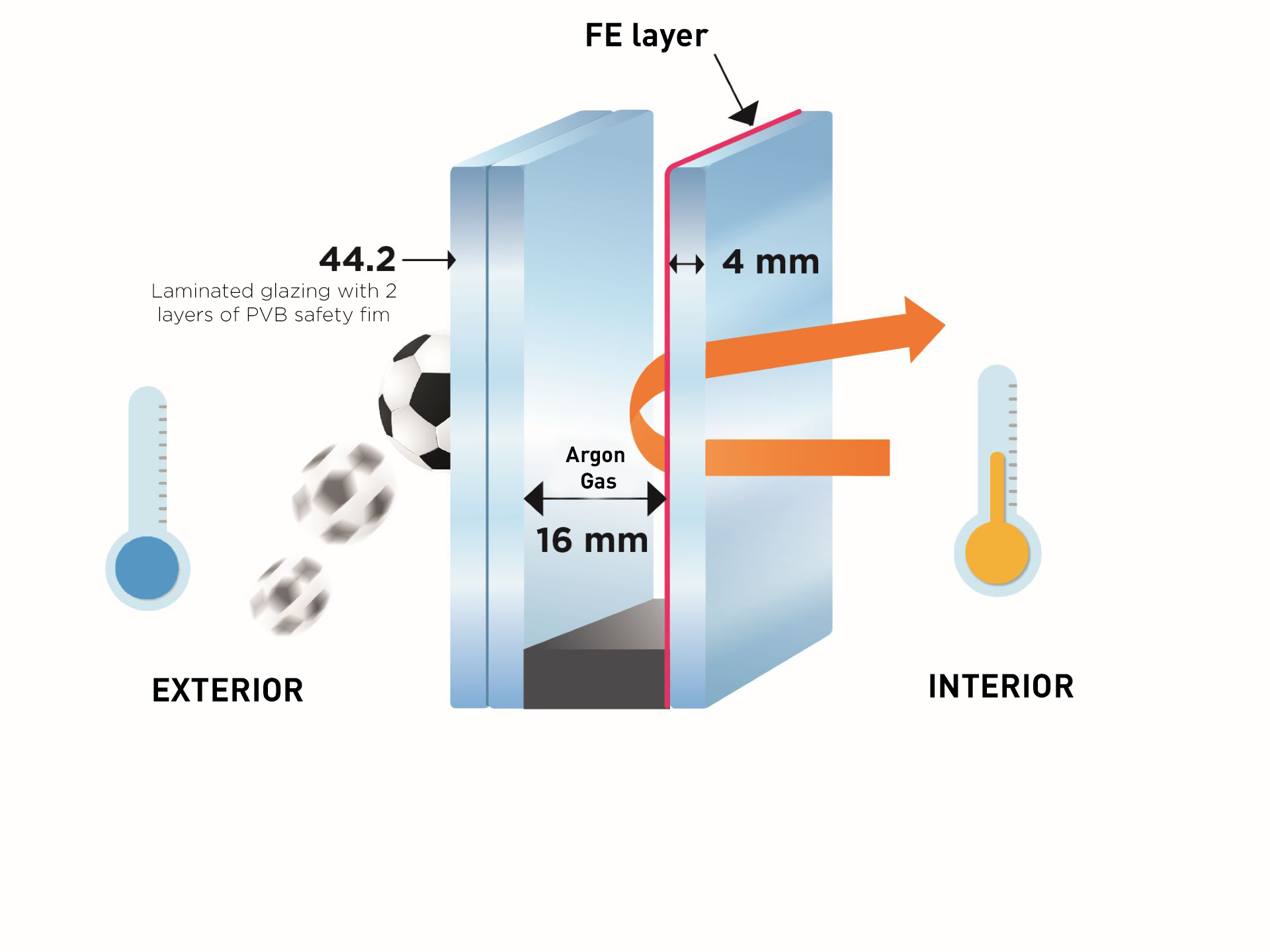
Example of laminated glazing composition
Composition type 44.2 / 16 Argon / LE 4
- Thermal insulation Ug = 1.1 W/(m².K)
- Winter solar factor = 59%
- Light transmission = 80%
- Sound reduction Ra,tr = 31 dB
- Security class P2A
| Type of glazing | Description | Class according to standard NF EN12600 | Class according to standard NF EN356 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4mm | Standard flat glass | Not defined | Not defined |
| 4mm | Tempered glass | 1C3 | Not defined |
| 22.1 | Laminated glass, 2 layers of 2mm glass + 1 PVB security or PVB silence interlayer | 2B2 | P1A - Protection against unorganized vandalism |
| 33.2 PLUS | Laminated glass, 2 layers of 3mm glass + 2 PVB security interlayers | 1B1 | P2A - Protection against unorganized vandalism |
| 44.2 | Laminated glass, 2 layers of 4mm glass + 2 PVB security or PVB silence interlayers | 1B1 | P2A - Protection against unorganized vandalism |
| 44.6 | Also called SP510, laminated glass, 2 layers of 4mm glass + 6 PVB security interlayers | 1B1 | P5A - Protection against break-ins |
Useful link: To complete your information, discover our safety selection guide for joinery, click here.
Acoustic glazing:
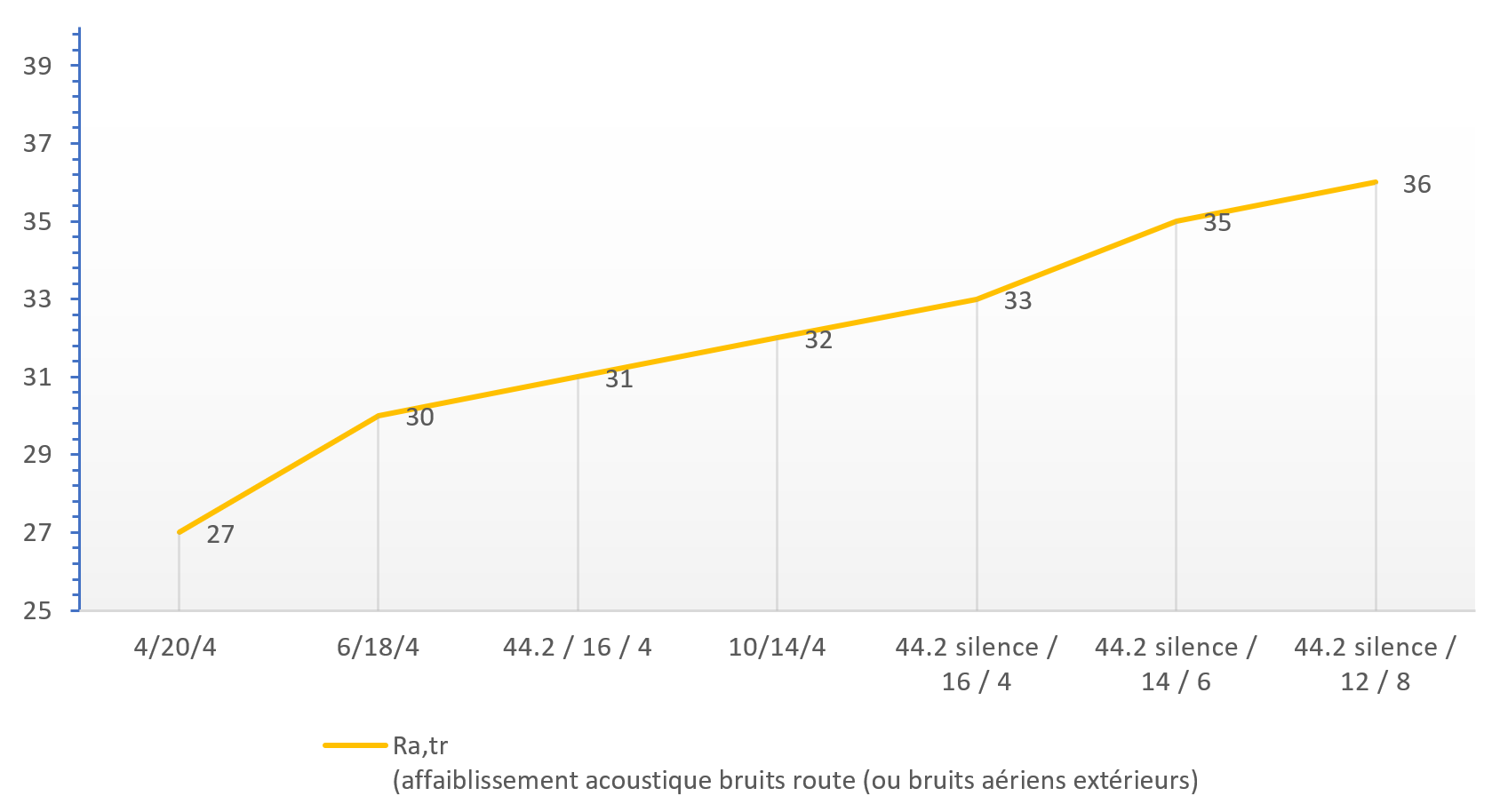
Noise pollution is a major source of discomfort. Spontaneously, more than three out of four French people admit to being disturbed by noise in their homes. Choosing the right glazing can significantly reduce the disturbances caused by external noises.
Among the factors that influence the acoustic performance of glazing, the following should be considered:
- The thickness of the glass in the glazing: The thicker the glass, the greater the sound attenuation.
- The asymmetry of the faces of the double glazing: Installing glass panes of different thicknesses on the interior and exterior sides of the double glazing helps "break" sound waves and limit their reverberation.
- The use of laminated glass faces with PVB security films, or better yet, PVB silence films specifically designed for acoustic performance, helps control the thickness and weight of the glazing and also increases noise attenuation. PVB silence films offer the dual benefit of enhanced acoustic performance and increased security.
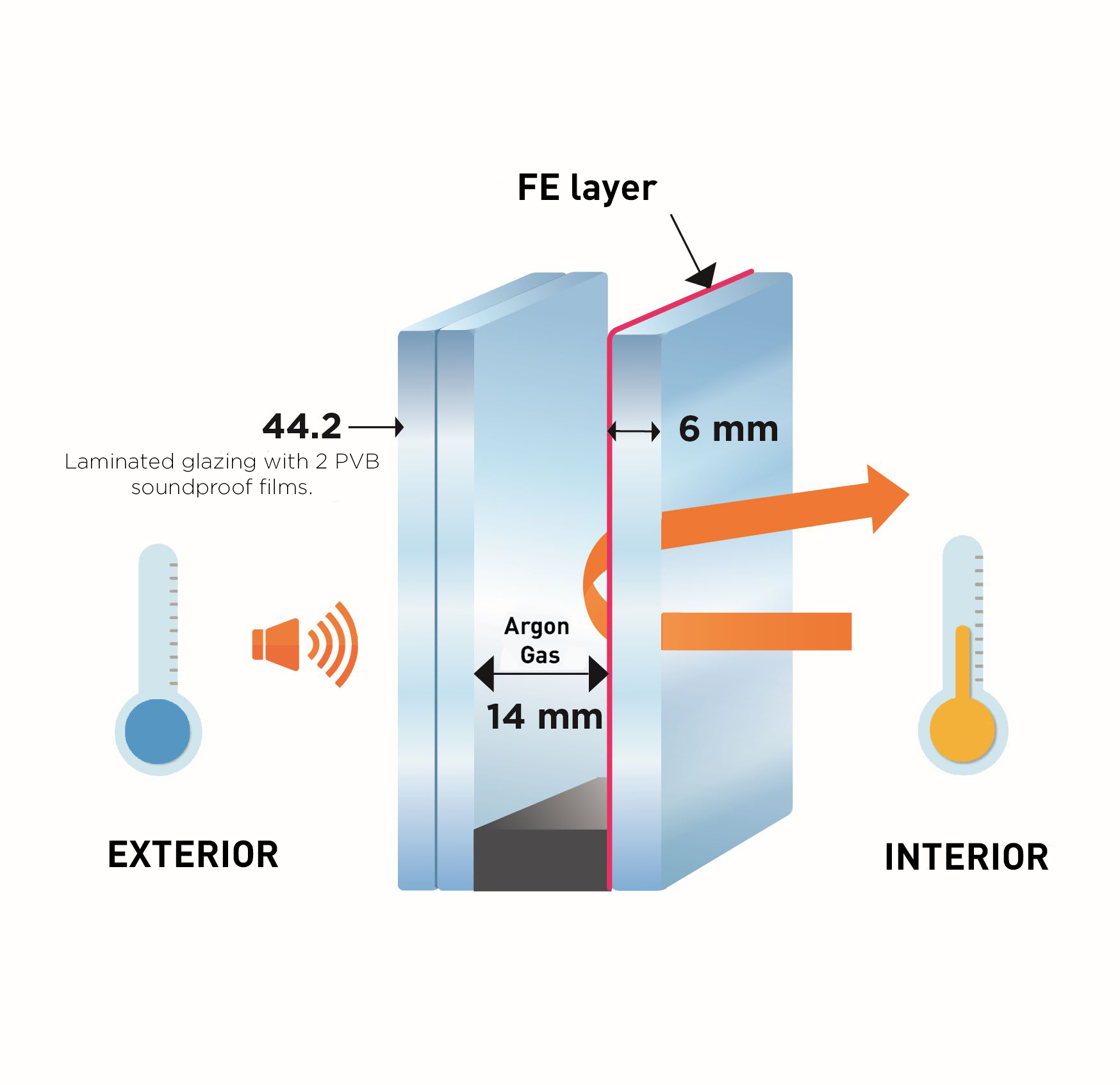
Example of acoustic glazing composition
Composition type 44.2 silence / 14 Argon / LE 6
- Thermal insulation Ug = 1.1 W/(m².K)
- Winter solar factor = 59%
- Light transmission = 80%
- Sound reduction Ra,tr = 35 dB
- Security class P2A
Axis 3. THE APPEARANCE:
To manage privacy or add an aesthetic touch, choose decorative glazing.
- Frosted satin glazing: Uniform appearance for enhanced privacy
- Printed glazing such as Granité 200, Delta Clair, and Delta Mat for a veined appearance, Pixarena, and Master Carré for their graphic look.
- Reflective glazing (note: these give a mirror-like appearance during the day for privacy, but this effect reverses at night when the interior of the home is lit).
Decorative glazing for privacy or aesthetics:

Frosted satin

Pixarena

Printed G200

Delta Clear

Delta Matte

Master square

Clear reflective

Silver reflective
The 3 AXES (energy needs / function / appearance) are usually combinable and compatible with each other. Therefore, an almost limitless number of glazing compositions can be offered to you. Consult your professional contact to benefit from the glazing best suited to your needs.
Glazing spacers or separators:
The glazing spacer serves the function of maintaining a constant gap between the two panes of double glazing. Traditionally, it is made of aluminum, which has the drawback of being highly conductive and increasing thermal losses between the glazing and the window frame by creating a thermal bridge.
To counter this disadvantage and avoid condensation issues, it can be replaced by a more efficient composite version, often called Warm-Edge (WE) or warm edge. We offer:
- Warm-Edge type TGI
- Warm-Edge type Swisspacer Ultimate
The filling of double glazing:
By default, all our glazing is filled with argon gas. This noble gas has thermal insulation properties that significantly reduce heat loss by convection compared to air.
For constructions at high altitudes, above 900 meters, pre-balancing may be necessary due to the lower atmospheric pressure. In this case, the glazing is put under vacuum specifically to prevent bulging of the faces of the double glazing.
And once at your home:
Almost all the glazing installed in our windows, patio doors, and sliding doors are identified by a unique Naviglass code. This 12-character code is directly printed on the spacer of the double glazing and allows you to find all the useful information about your glazing: composition, start date of warranty, performance.