Windows and Energy Efficiency
"I want to save energy."
Reducing heating costs and improving home comfort are the two main goals when replacing doors and windows. The Uw coefficient measures the energy loss of the entire frame + glazing unit. The lower the Uw value, the better the thermal performance of your windows, helping to reduce your energy bill.
FOCUS ON
THERMAL PERFORMANCE
The desire to save on heating and improve home comfort is often the main reason for replacing windows. However, thermal performance is not the only factor to consider. In addition to the Uw coefficient, which defines a window’s thermal efficiency, you should also take into account your potential needs for air conditioning or lighting.
HOW IS IT MEASURED?
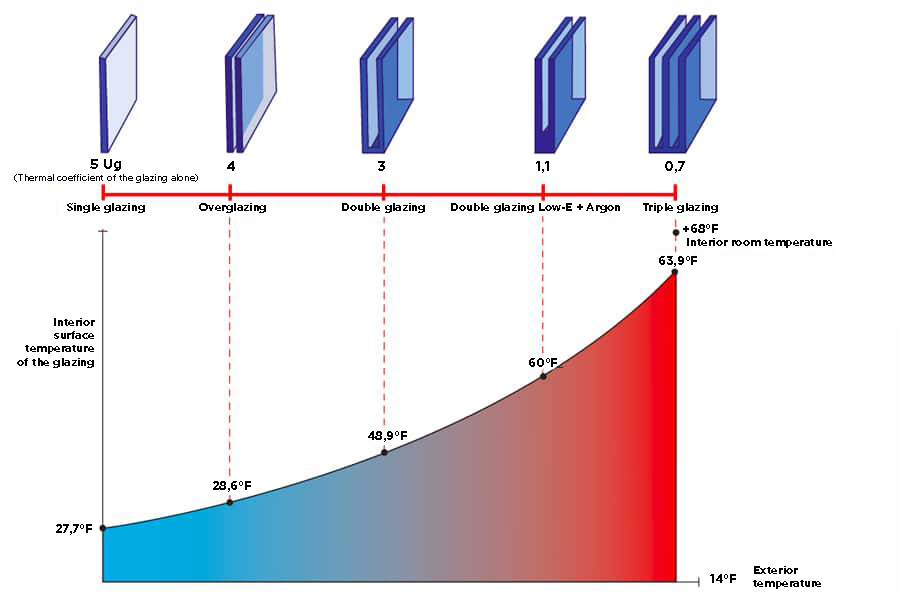
Thermal insulation is defined by the Uw coefficient, which represents heat loss to the outside. The higher this value, the greater the heat loss. When a movable protection, such as a roller shutter, is present, the Uws coefficient is used instead.
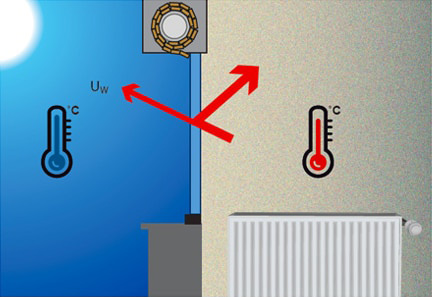
Mobile protection absent or raised (Uw)
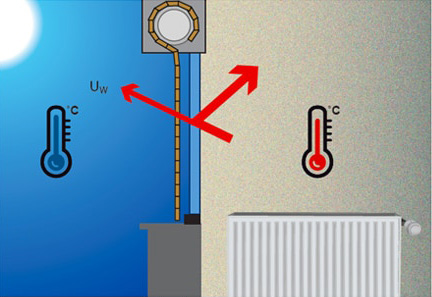
Closed mobile protection (Uws)
HOW TO INTERPRET IT?
The values found in this catalog are all calculated based on a standardized size (known as Acotherm) and a standardized installation method to allow for an objective comparison across different ranges. However, the Uw coefficient is calculated for each window individually, depending on its size, glazing, and composition. Significant variations can arise based on these factors—for example, the effect of window composition on Uw. It is clear that prioritizing larger glass surfaces improves thermal performance.
HOW TO IMPROVE IT?
• Double glazing:
A two-pane glass unit with an air gap, featuring a Low-Emissivity (Low-E) coating that enhances thermal insulation. Some Low-E coatings provide reinforced insulation or more effectively limit solar gains. The glazing is filled with argon gas, further improving thermal efficiency. The spacer bar, which connects the two panes, also plays a crucial role. A composite Warm-Edge spacer, an alternative to the traditional aluminum spacer, reduces the thermal bridge between the frame and the glass, ultimately enhancing the window's overall thermal performance.
> Learn more about glazing

• Triple glazing:
More efficient in terms of thermal insulation than double glazing, the addition of a third pane and a second air gap reduces solar gains. It is mainly used on façades with little sun exposure. However, specific Low-Emissivity coatings or the use of extra-clear glass can help increase solar gains.
• Roller shutters:
The Uws coefficient considers the insulating effect of the shutter slats. To assess the insulation capacity of the roller shutter box, the Uc coefficient is used, which is independent of Uws. Mhttps://groupe-millet.com/produits-complementaires/volets-roulants-et-motorisations/ILLET offers optional insulation levels for shutter boxes, with values reaching up to Uc = 0.71 W/(m²·K).
> Learn more about roller shutters